Testkube Cloud Control Plane
If you don't want to host the Testkube Control Plane in your infrastructure, you can use the Cloud Control Plane provided by the Testkube team at https://app.testkube.io. In this scenario, you only have to install Testkube Agent(s) in your infrastructure wherever you want to run your tests.
Getting Started
To get started with the Cloud Control Plane, go to https://app.testkube.io and sign up for a trial account. During the onboarding, you will be prompted to create an initial Testkube Environment, which will provide you with the required CLI/Helm commands to deploy the corresponding Testkube Agent in your infrastructure. You can then add as many Environments as you need to execute your Tests in your infrastructure accordingly - Read More.
For local deployment of the Agent (for example during evaluation) you can either use the Testkube Docker Agent or create your own local Kubernetes cluster - Read More.
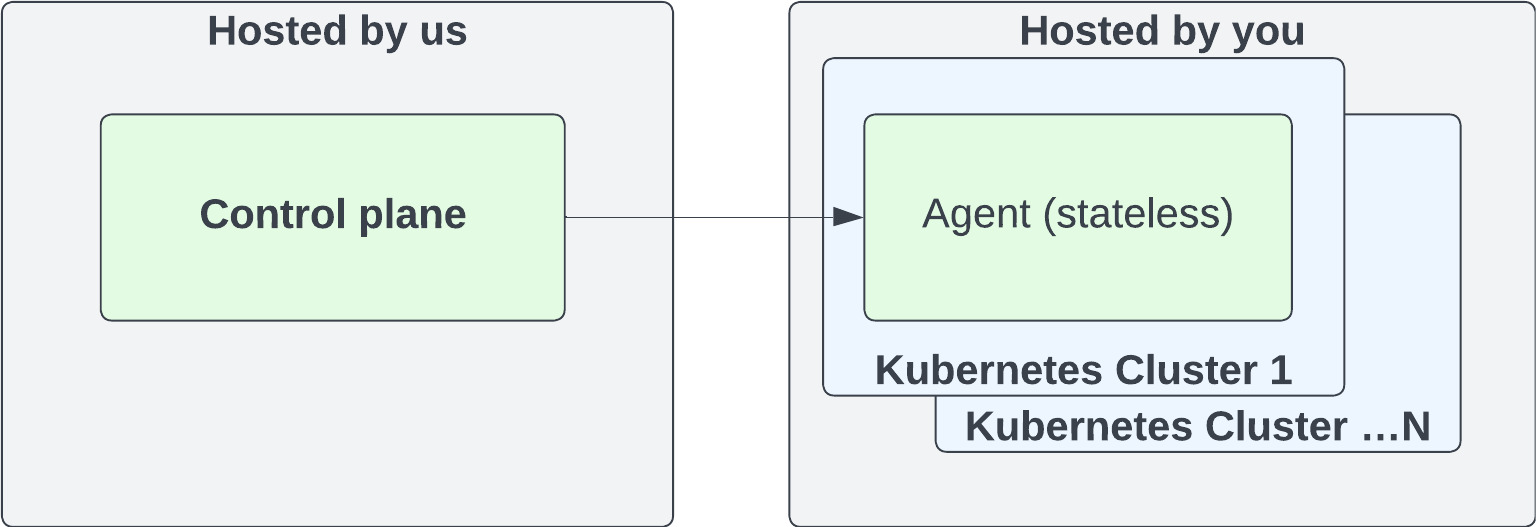
Deployment Architecture
A high-level deployment architecture for the Testkube Cloud Control Plane is shown below.
Network traffic control
Egress
To allow the agent to connect to the Control Plane, you will need to allow
egress connections to the agent.testkube.io host on port 443. If this
connection is proxied, make sure the proxy supports HTTP/2 as the agent uses
a bidirectional gRPC connection to communicate with the control plane and that
works best over HTTP/2.
Test executions will need to send artifacts and logs to a Cloud Storage bucket
on GCP so egress traffic to the storage.googleapis.com host on port 443
should also be allowed.
Testkube includes a background service that checks the latest Agent version by
querying the GitHub Releases API. In environments with restricted egress,
allow access to api.github.com or disable the check by setting
DISABLE_AGENT_VERSION_CHECK=true on the Testkube Enterprise API:
testkube-cloud-api:
additionalEnv:
DISABLE_AGENT_VERSION_CHECK: true
The check is informational only and does not affect core functionality. For offline installations, it is disabled by default.
Ingress
When using the Testkube Cloud Control Plane, all network traffic is initiated from the Agent to the Control Plane. If you are using a stateful firewall you will not need to add any additional ingress rules, but if not then you will need to allow ingres connections on the ephemeral ports for your particular OS.