Test Workflows Examples - Basics
The Schema Reference for Test Workflows describes all available properties and constructs
Running the Image
The Test Workflows spec allows you to provide instructions in setup, steps and after properties.
Syntax
Both setup, steps and after have the same syntax - they are a list of steps. The step is an object that has execution instructions.
apiVersion: testworkflows.testkube.io/v1
kind: TestWorkflow
metadata:
name: overview--example-1
spec:
steps:
- run:
image: "curlimages/curl:7.78.0"
args:
- "https://testkube.io"
Running the Image
Use a run instruction that has similar syntax to the native Kubernetes’ container. A command exiting with code > 0 is considered a failure.
Using Shell
Running Shell Commands
For simplicity, you can also run shell commands with the run instruction and the shell property.
The script is automatically prepended with set -e, so, by default, it will fail the step on any error.
apiVersion: testworkflows.testkube.io/v1
kind: TestWorkflow
metadata:
name: overview--example-2
spec:
steps:
- run:
image: "curlimages/curl:7.78.0"
shell: |
curl https://testkube.io
Alternative Syntax
Alternatively, you can use shell directly as an instruction and a default image will be used.
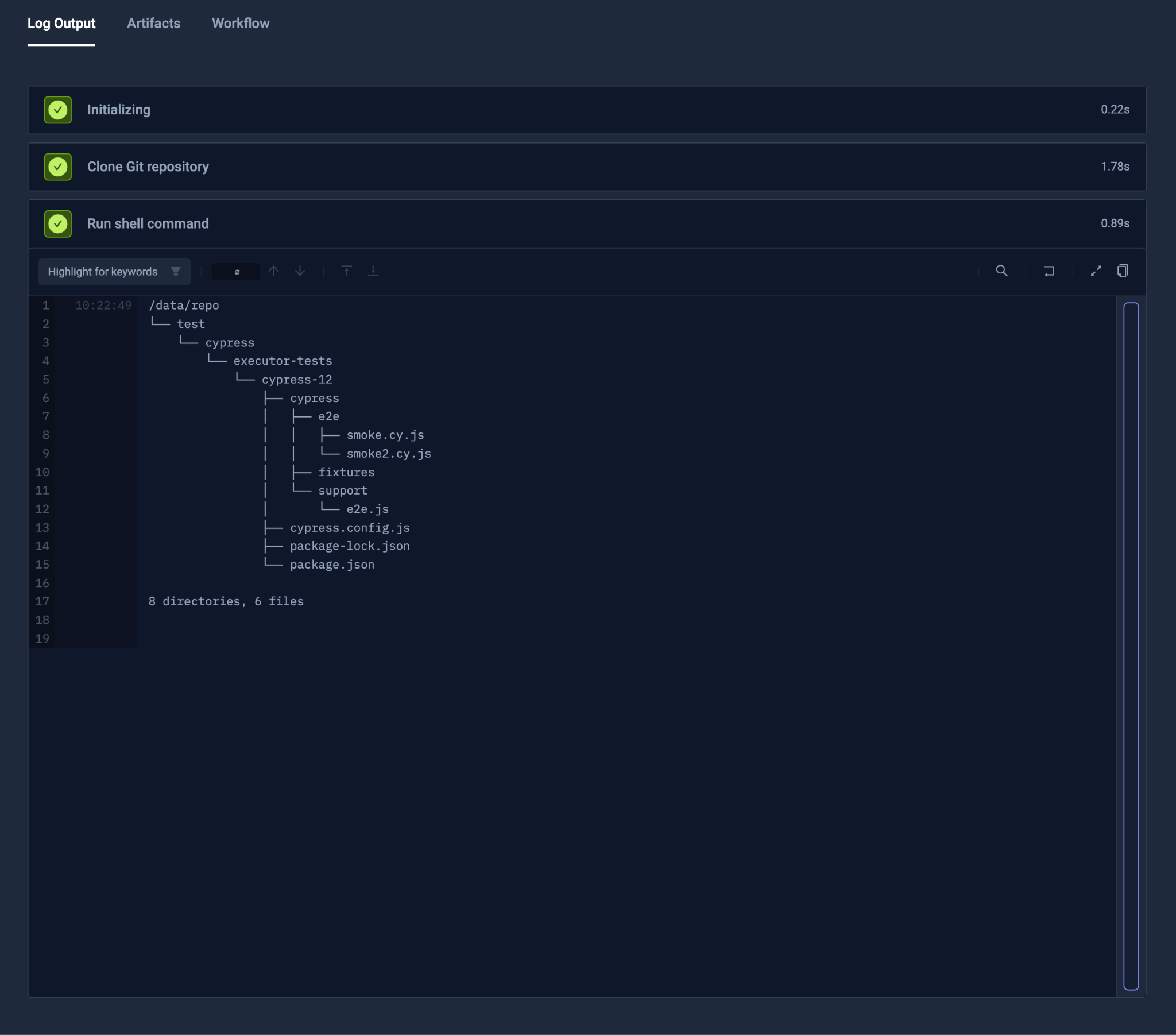
Fetching the Git Repository
Read more about content from Git repositories at Git Repository.
Fetching Data from Git
To fetch data from the Git, use the git property of content. You may provide the address, revision (commit, branch or tag), along with i.e. token.
To avoid fetching all files in mono-repository, you can use paths for sparse checkout.
apiVersion: testworkflows.testkube.io/v1
kind: TestWorkflow
metadata:
name: overview--example-3
spec:
content:
git:
uri: "https://github.com/kubeshop/testkube"
revision: "main"
paths:
- "test/cypress/cypress-12"
steps:
- shell: "tree /data/repo"
Mounting
By default, the repository is mounted to /data/repo directory. You can control it with mountPath property though.
Fetching a Secured Git Repository
Using a Token from a Secret
You may provide the Git token and username either as plain-text, or via the tokenFrom and usernameFrom clauses that are the same as native Kubernetes env.*.valueFrom.
apiVersion: testworkflows.testkube.io/v1
kind: TestWorkflow
metadata:
name: overview--example-4
spec:
content:
git:
uri: "https://github.com/kubeshop/testkube"
tokenFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: "private-repo-secret-token"
key: "token"
steps:
- shell: "tree /data/repo"
Using Multiple Steps
Running Multiple Steps
To run multiple steps, add another step with the next instructions.
apiVersion: testworkflows.testkube.io/v1
kind: TestWorkflow
metadata:
name: overview--example-5
spec:
content:
git:
uri: "https://github.com/kubeshop/testkube"
revision: "main"
paths:
- "test/cypress/cypress-12"
steps:
- name: "Install dependencies"
run:
image: "cypress/included:13.6.4"
workingDir: "/data/repo/test/cypress/cypress-12"
shell: "npm install"
- name: "Run test"
run:
image: "cypress/included:13.6.4"
workingDir: "/data/repo/test/cypress/cypress-12"
shell: "cypress run"
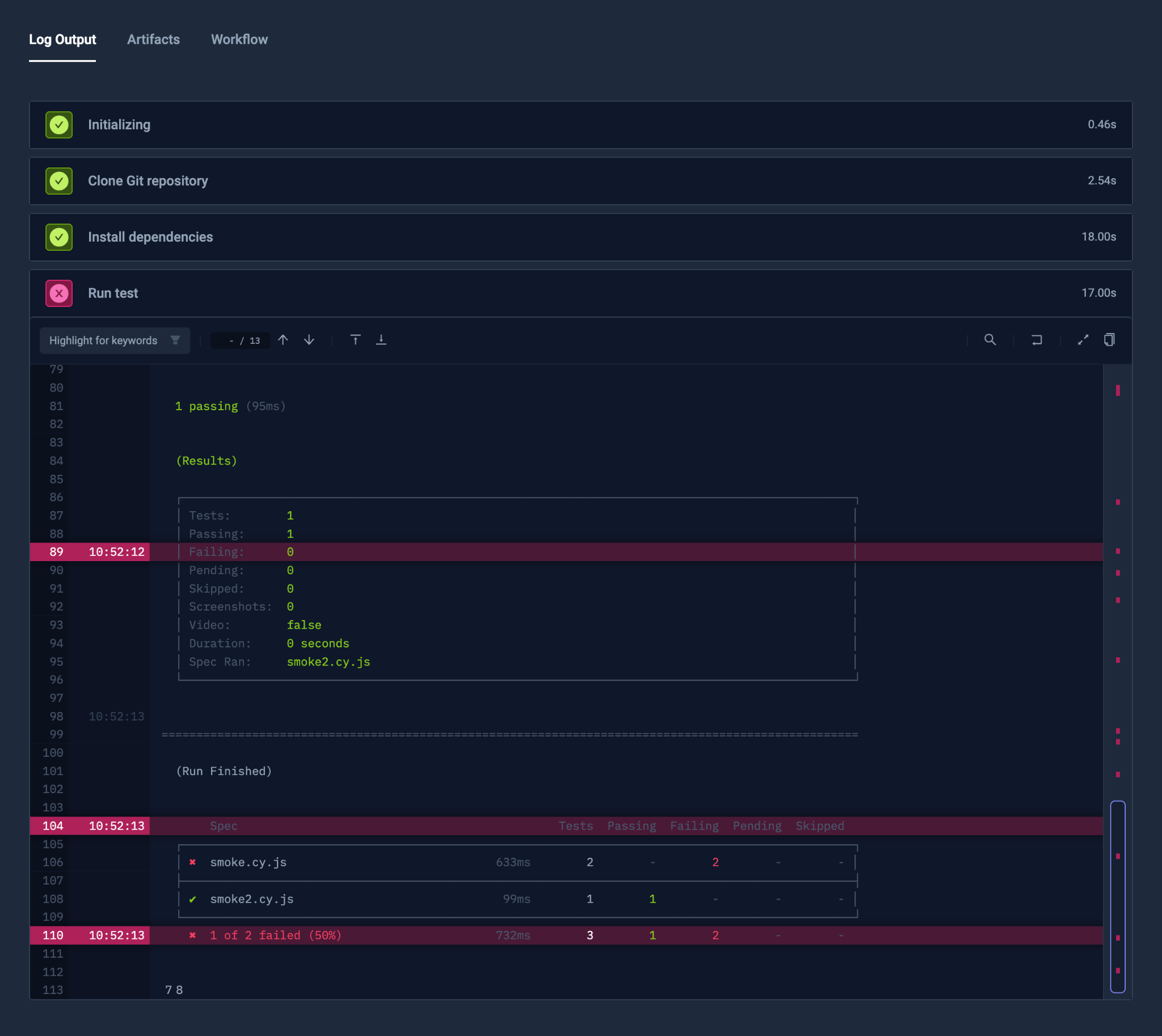
Container Defaults
Setting Up Defaults
To configure default container settings, you may use the container property.
It has a similar syntax to the Kubernetes’ native Container spec.
apiVersion: testworkflows.testkube.io/v1
kind: TestWorkflow
metadata:
name: overview--example-6b
spec:
content:
git:
uri: "https://github.com/kubeshop/testkube"
revision: "main"
paths:
- "test/cypress/cypress-12"
container:
image: "cypress/included:13.6.4"
workingDir: "/data/repo/test/cypress/cypress-12"
resources:
requests:
memory: "2Gi"
cpu: 2
steps:
- name: "Install dependencies"
shell: "npm install"
- name: "Run test"
shell: "cypress run"
Notable Nuances
Thanks to the container and run instructions being similar to native Kubernetes’ container specs, you can easily set the required resources for running.
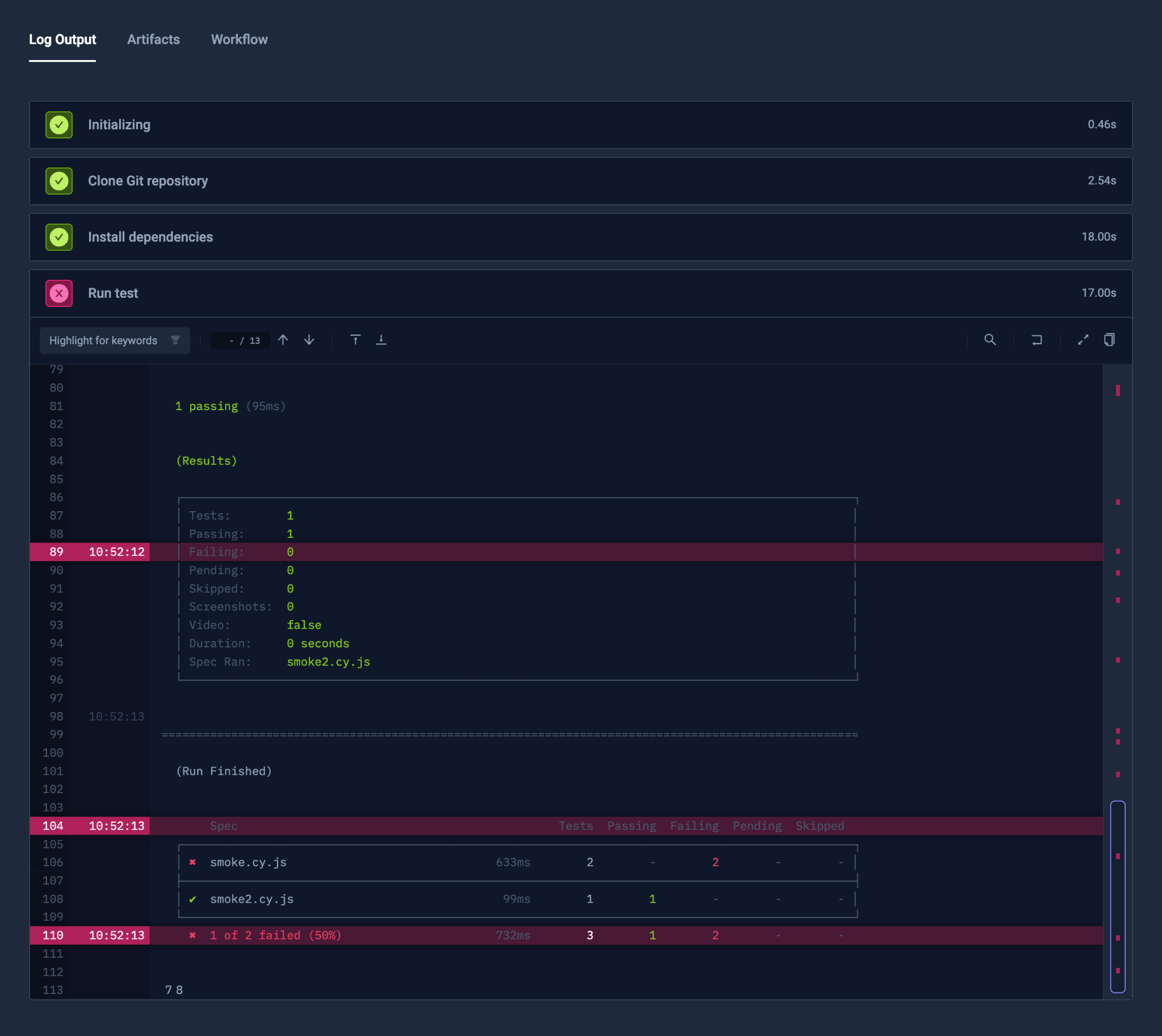
Step Isolation
Nested Steps
You can also pass nested setup steps in the step list.
apiVersion: testworkflows.testkube.io/v1
kind: TestWorkflow
metadata:
name: overview--example-7
spec:
steps:
- name: "Run test"
content:
git:
uri: "https://github.com/kubeshop/testkube"
revision: "main"
paths:
- "test/cypress/cypress-12"
container:
image: "cypress/included:13.6.4"
workingDir: "/data/repo/test/cypress/cypress-12"
steps:
- name: "Install dependencies"
shell: "npm install"
- shell: "cypress run"
Content and Defaults
Defaults configured in the step will work similarly to top-level defaults but will be accessible only by the step itself and all steps inside. For example, previous and subsequent steps will not have access to mounted repositories or environment variables.
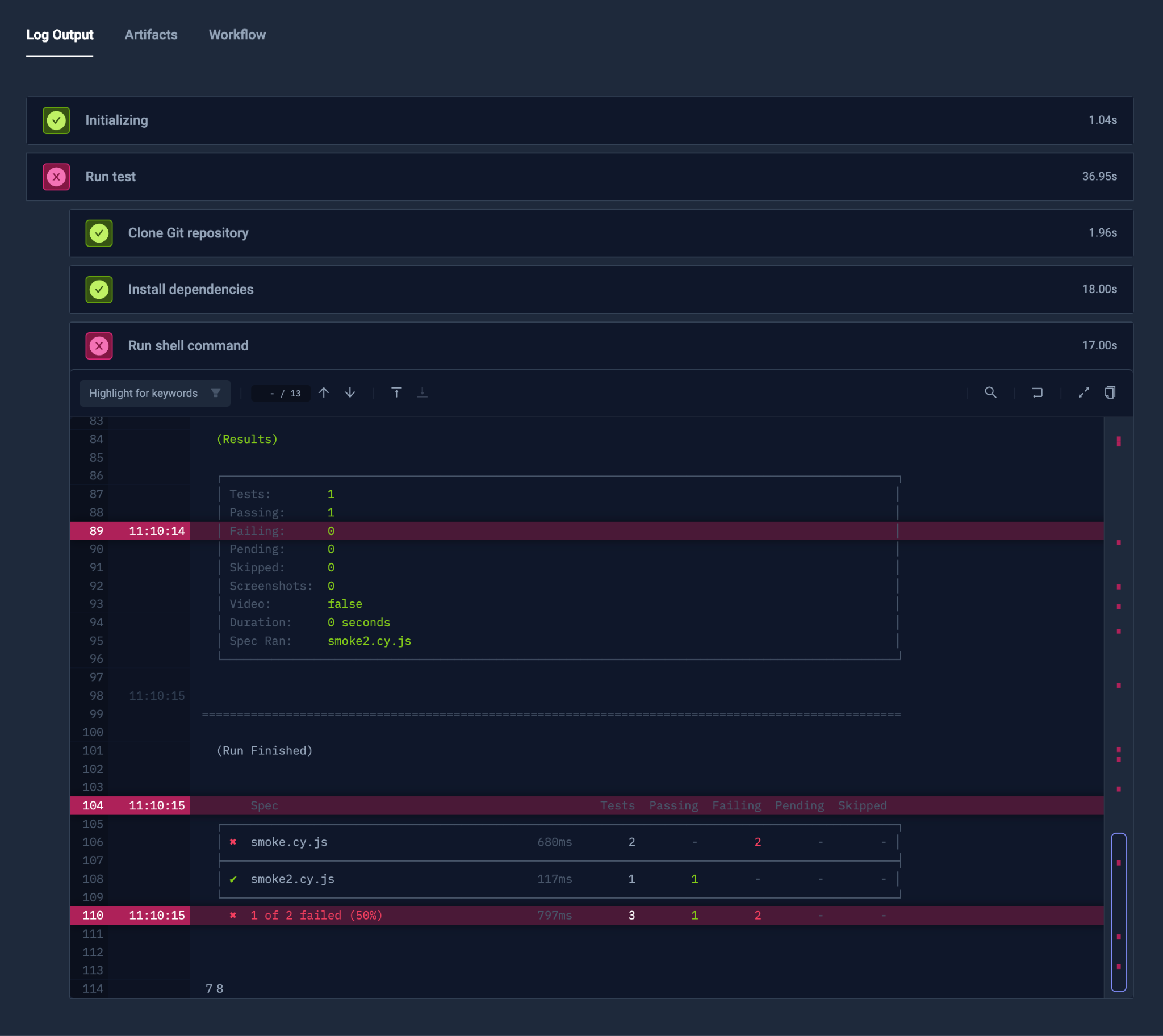
Step Orchestration
Optional Steps
You can add optional: true for a step, so that it will not affect the outcome of the orchestration.
apiVersion: testworkflows.testkube.io/v1
kind: TestWorkflow
metadata:
name: overview--example-8
spec:
steps:
- name: "Step 1"
optional: true
shell: exit 1
- name: "Step 2"
negative: true
shell: exit 1
- name: "Step 3"
negative: true
shell: exit 0
- name: "Step 4"
shell: echo hello
- name: "Step 5"
condition: always
retry:
count: 3
shell: echo foo; exit 1
Conditional Steps
By default, the next step will run only when the previous steps have succeeded. This can be controlled with the condition property.
As an example, condition: always will cause the step to always be executed, even if the previous step has failed.
Retry Mechanism
It’s possible to automatically retry the step on a failure (or any other condition).
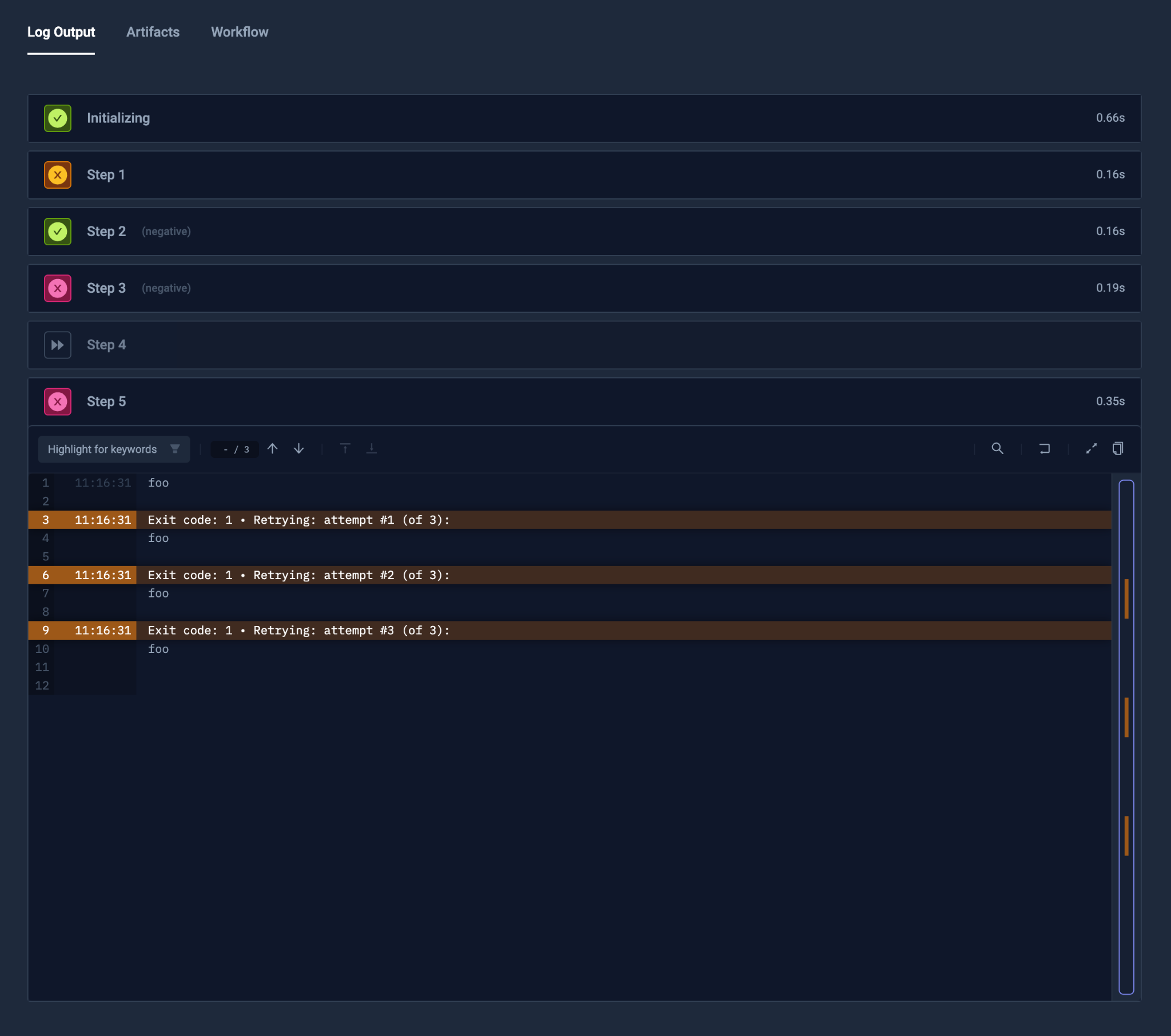
Step Timeout
Steps can have individual timeout values to constrain their execution time. If the timeout is exceeded, the step and containing Workflow fail accordingly.
The regex-pattern for the timeout is
^((0|[1-9][0-9]*)h)?((0|[1-9][0-9]*)m)?((0|[1-9][0-9]*)s)?((0|[1-9][0-9]*)ms)?$
so valid values include 10s, 1m, 1h30m, 500ms, etc.
If you want to ensure that steps after a step with a timeout always execute, either mark the step as optional or mark the following steps with condition: always.
Step Delay
It is possible to delay the execution of the step with the delay property, which follows the same
syntax as the timeout property above.
For example, the following step will be executed after 10 seconds.
apiVersion: testkube.io/v1
kind: TestWorkflow
metadata:
name: delay-example
spec:
steps:
- name: Step 1
delay: 10s
shell: echo hello
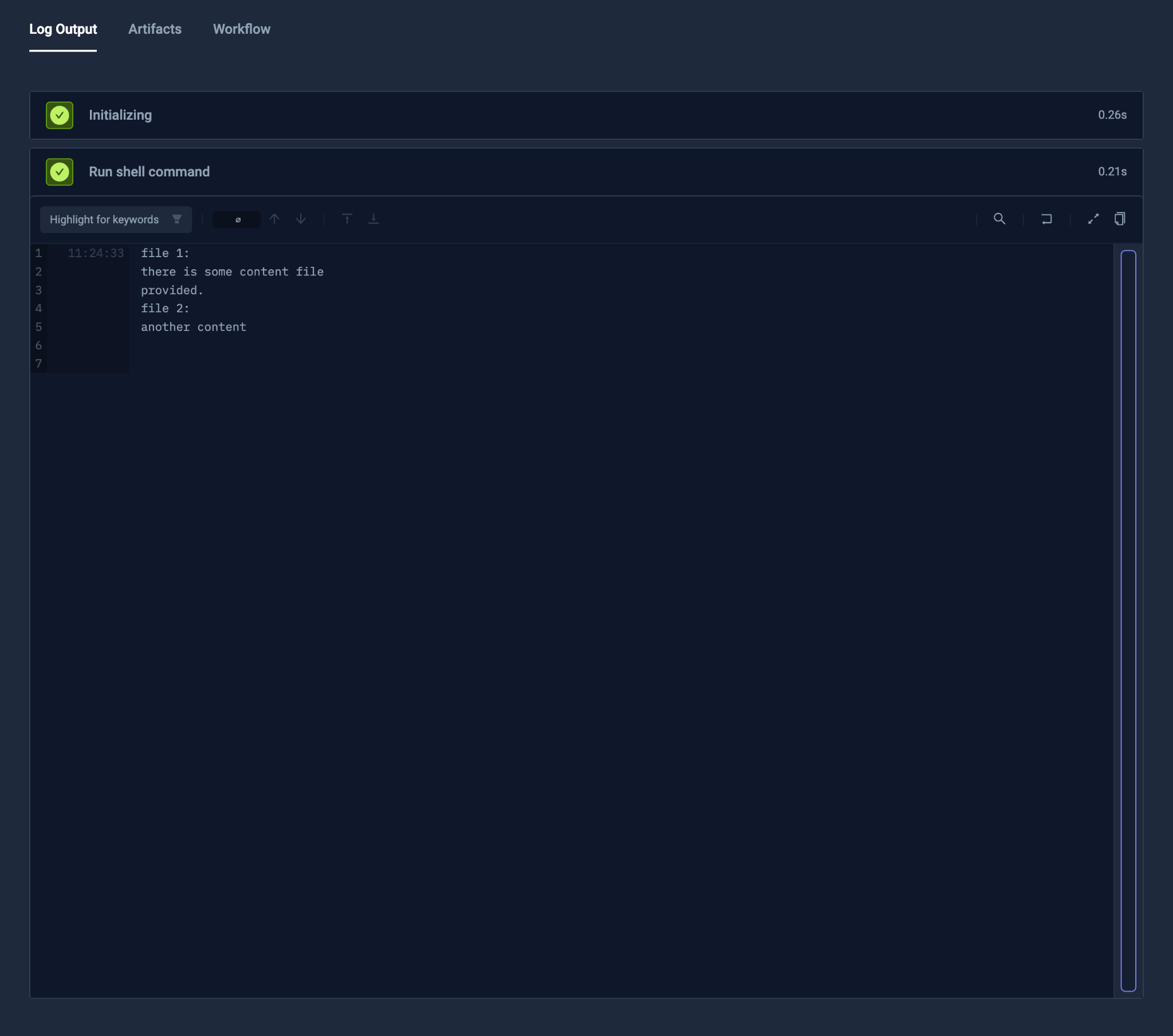
Content Files
Provide Static Files
Apart from the Git repository and regular commands, a Test Workflow can use static files directly from the spec - Read More.
These files are mounted from a ConfigMap automatically (unless, instead of content, there is contentFrom used
with a similar schema as Kubernetes’ env.\*.valueFrom).
When the path is relative, it will be mounted in the container’s working directory.
apiVersion: testworkflows.testkube.io/v1
kind: TestWorkflow
metadata:
name: overview--example-9
spec:
content:
files:
- path: /some/path
content: |
there is some content file
provided.
- path: another-file.txt
content: |
another content
steps:
- workingDir: /foo/bar
shell: |
echo "file 1:"
cat /some/path
echo "file 2:"
cat another-file.txt
Artifacts
Saving the Artifacts
Saving the artifacts is as simple as defining the artifacts instruction and providing the file masks to fetch.
There is no need to create additional volumes, the artifacts step has access to all the files - Read More.
apiVersion: testworkflows.testkube.io/v1
kind: TestWorkflow
metadata:
name: overview--example-10
spec:
content:
git:
uri: "https://github.com/kubeshop/testkube"
paths:
- "test/playwright/playwright-project"
container:
image: "mcr.microsoft.com/playwright:v1.32.3"
workingDir: "/data/repo/test/playwright/playwright-project"
resources:
requests:
memory: "2Gi"
cpu: 2
steps:
- shell: "npm ci"
- shell: "npx playwright test --workers 2 --reporter html"
- condition: always
artifacts:
paths:
- "playwright-report/**/*"
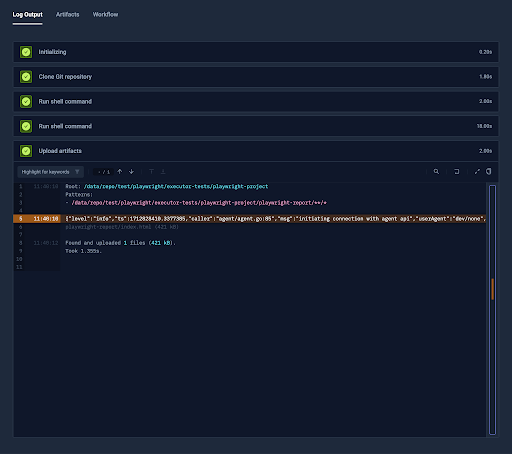
Test Suite Like Workflows
Run Dependent Test Workflows or Tests
To run other Test Workflows or Tests, you can use the execute instruction.
You can define the number of concurrent executions with parallelism as well.
apiVersion: testworkflows.testkube.io/v1
kind: TestWorkflow
metadata:
name: overview--example-11
spec:
steps:
- execute:
tests:
- name: "example-test"
workflows:
- name: "overview--example-3"
- name: "overview--example-5"
- name: "overview--example-8"
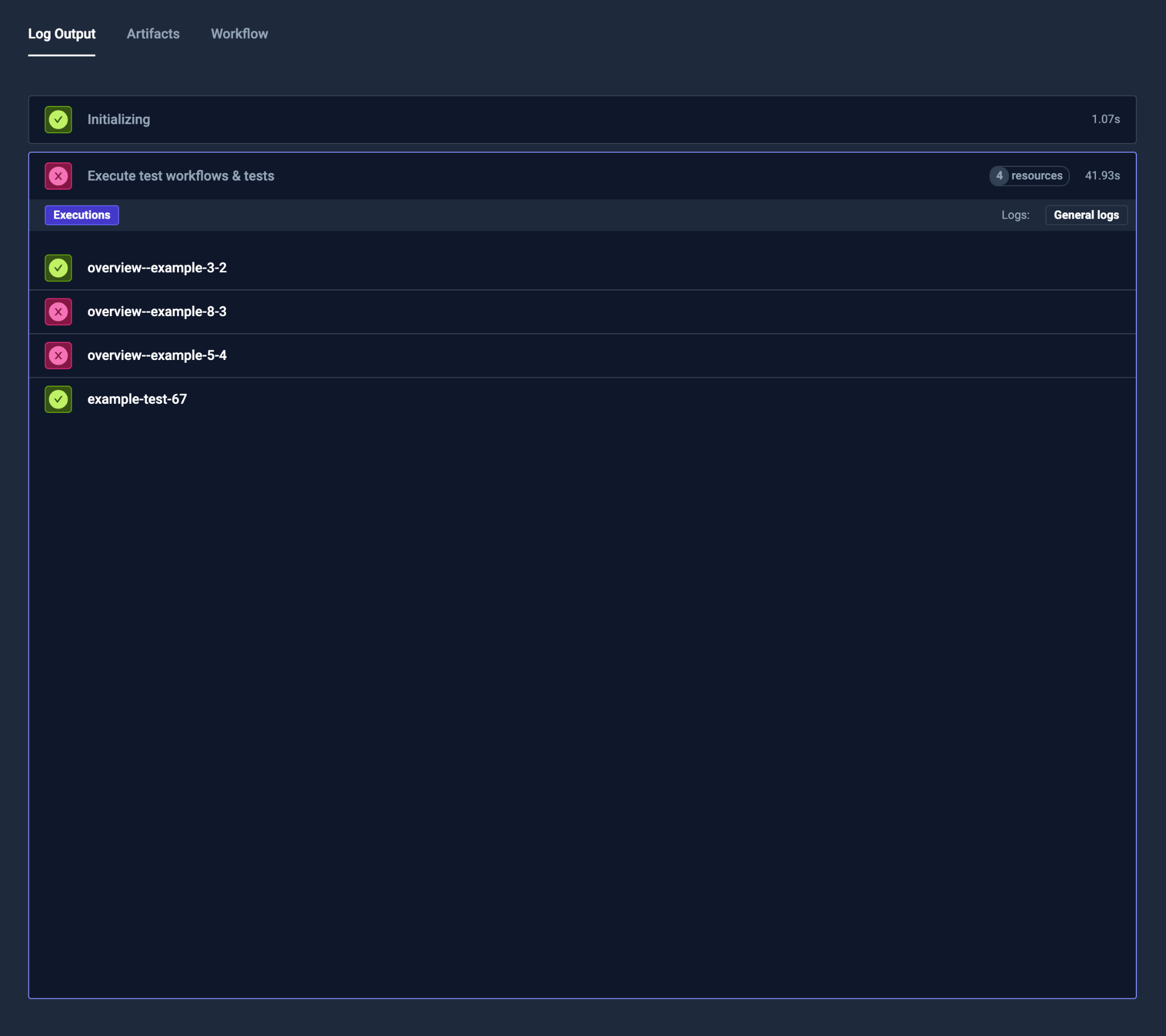
Read more about Workflow orchestration at Workflow Orchestration.
Job/Pod Configuration
Configuring the Job
By using the job property, you can configure labels, annotations and execution namespace of the Job.
In case of supplying a namespace, you will need to define execution namespaces in your Helm chart values - Read More.
It's possible to generate all required RBAC or just manually supply them.
apiVersion: testworkflows.testkube.io/v1
kind: TestWorkflow
metadata:
name: overview--example-12
spec:
job:
labels:
job-label: "foobar"
annotations:
this.is.important: false
namespace: "default"
Configuring the Pod
By using the pod property, you can configure labels, annotations, serviceAccountName, imagePullSecrets, volumes, or other properties of a PodSpec.
apiVersion: testworkflows.testkube.io/v1
kind: TestWorkflow
metadata:
name: overview--example-13
spec:
job:
labels:
job-label: "foobar"
pod:
labels:
pod-label: "barfoo"
serviceAccountName: "testkube-api-server"
imagePullSecrets:
- name: "dockerhub-secret"
Read more about Job and Pod configurations at Pod & Job
Additional Test Workflow Examples
Additional Test Workflow examples can be found under the Examples and Guides section in this documentation, and in the Testkube repository.