Workflow Details
Workflow Details provides a central location to run, monitor, and configure the Workflows in your Environment.
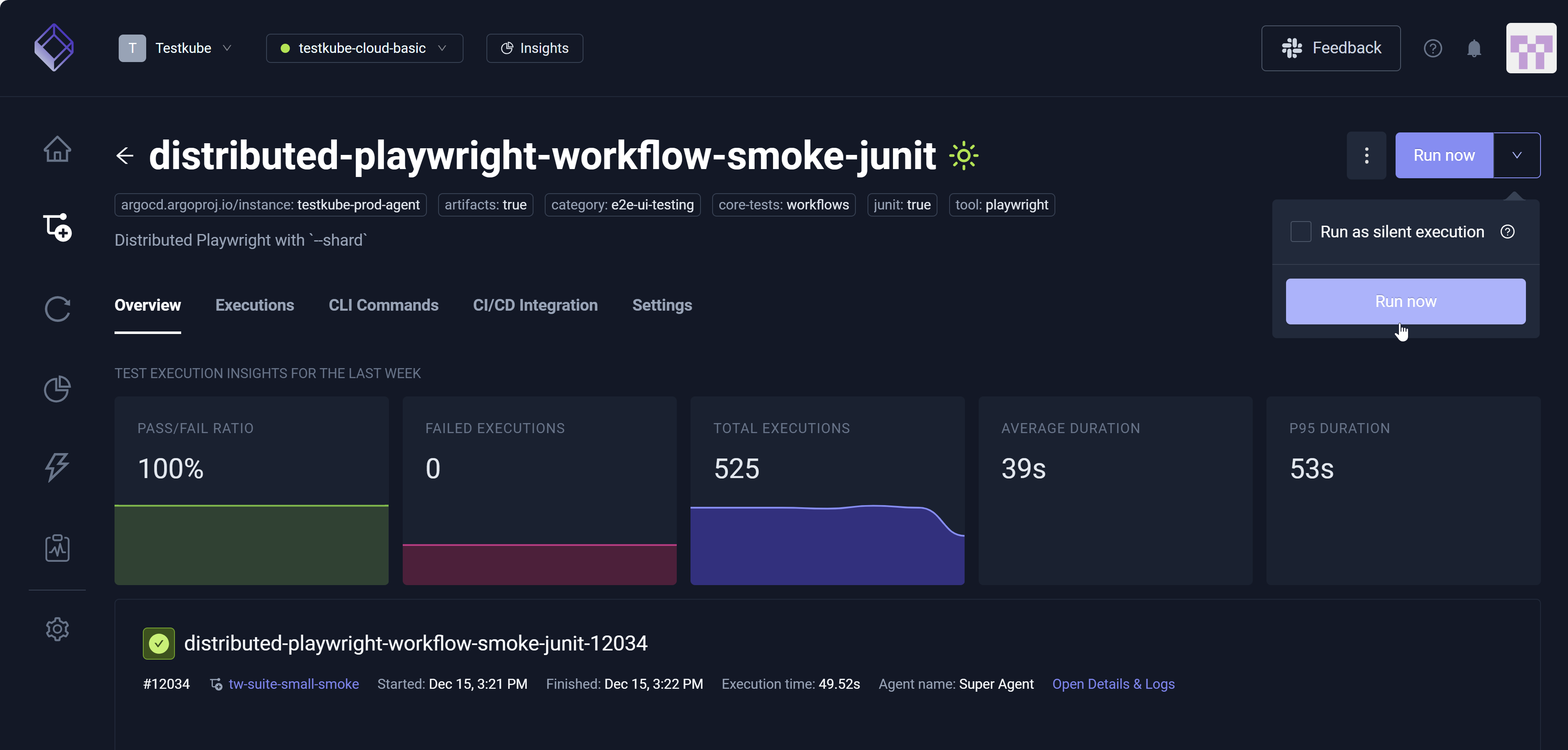
Running a Workflow
After you select a Workflow, you can view its details via the Overview, Executions, CLI Commands, CI/CD Integration, and Settings tabs. You can also access Run now (top right) to run the Workflow immediately. The Run now drop-down list box includes Run as silent execution. You can select this checkbox to run silent Executions, which do not trigger webhooks, events, or metrics collection. Therefore, the Execution completes normally; however, it is excluded from integrations, notifications, and monitoring systems that would otherwise respond to this run.
While you can select Run now from various tabs, it is common to run Workflows via CI/CD Integration and from Scheduling located within the Settings tab.
Workflows execute one or more tests; Composite Workflows execute one or more Workflows, with one orchestrating the others. The number of tests or Workflows that run is based on the testing tool you use.
A Runner Agent acts as the test Execution engine and runs within the Kubernetes cluster to spin up pods, facilitate the testing defined in Testkube, and report results. You can use multiple Runner Agents in your Environment. For additional information, read Runner Agents.
Overview Tab
The Overview tab displays Test Execution Insights for the Last Week to include the Pass/Fail Ratio, Failed Executions, Total Executions, Average Duration, and P95 Duration.
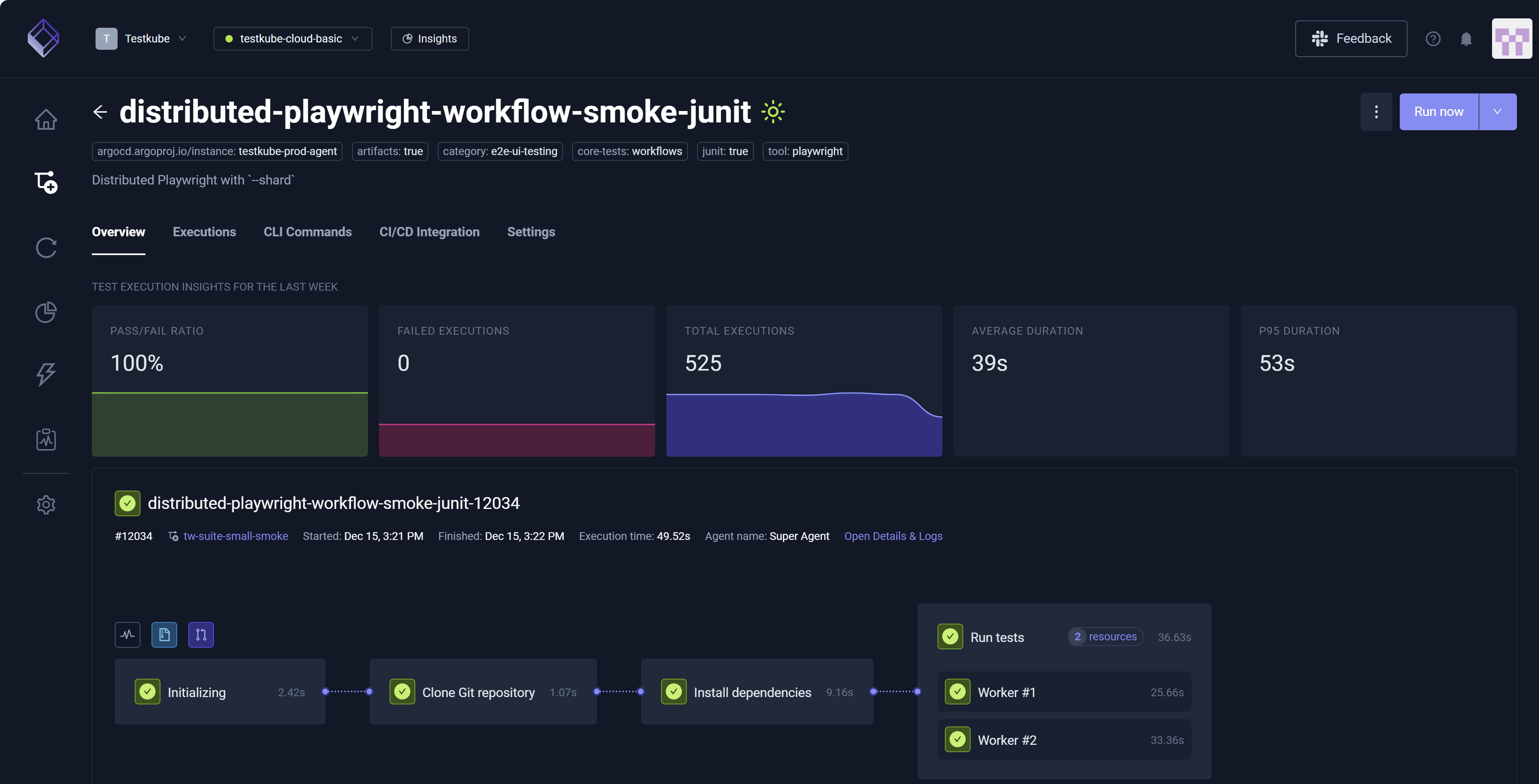
Upon selection, the Resource Usage, Artifacts and Content Sources icons (middle page) display additional Workflow details.
![]()
More results are available (lower page) along with a Reports visualization option. JUnit Reports, for example, generate based on the content of your YAML file. Adding arguments specific to JUnit reports trigger this report generation.
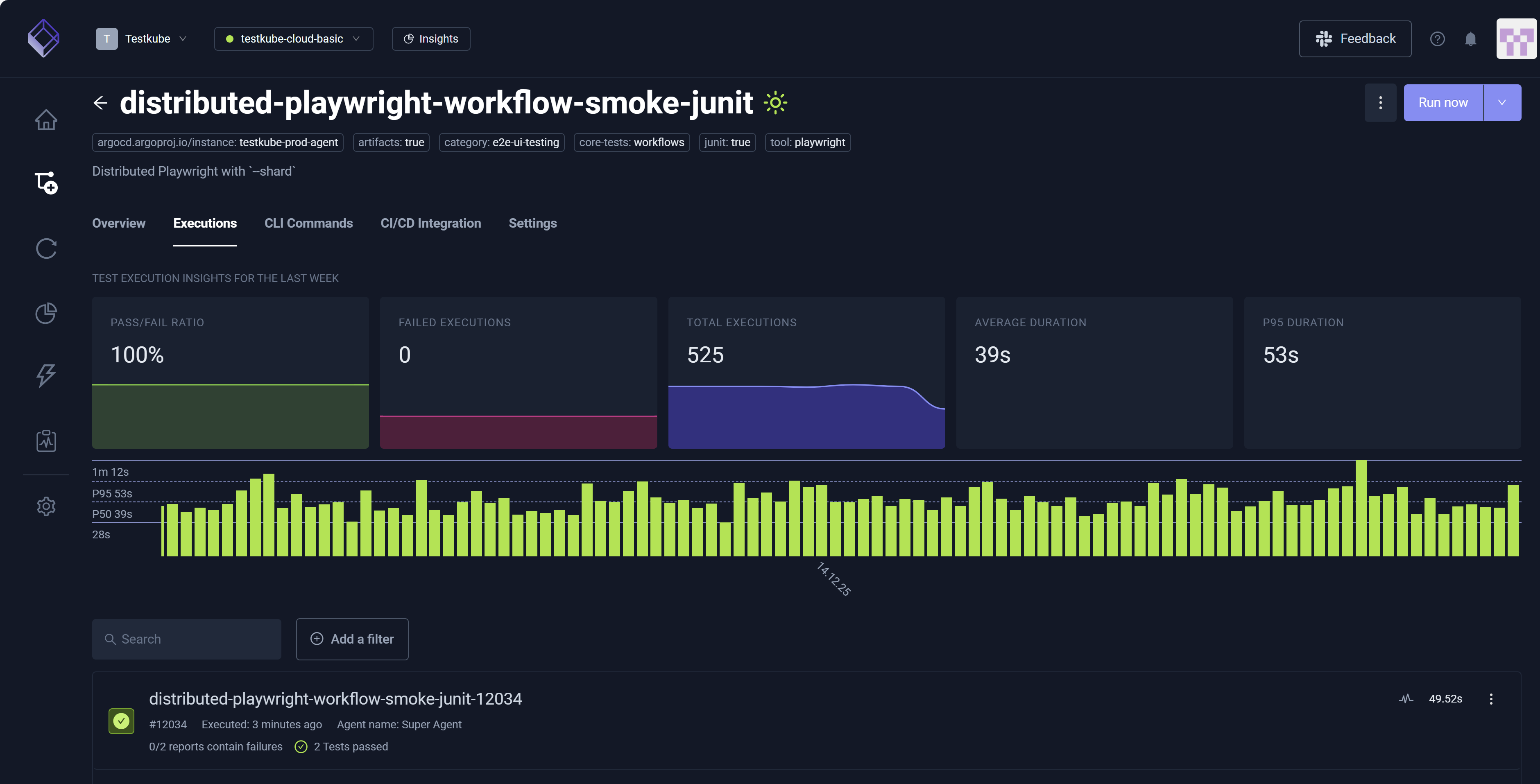
Executions Tab
The Executions tab displays Test Execution Insights for the Last Week along with Search and Add a filter. You can hover over each Execution to reveal additional metrics.
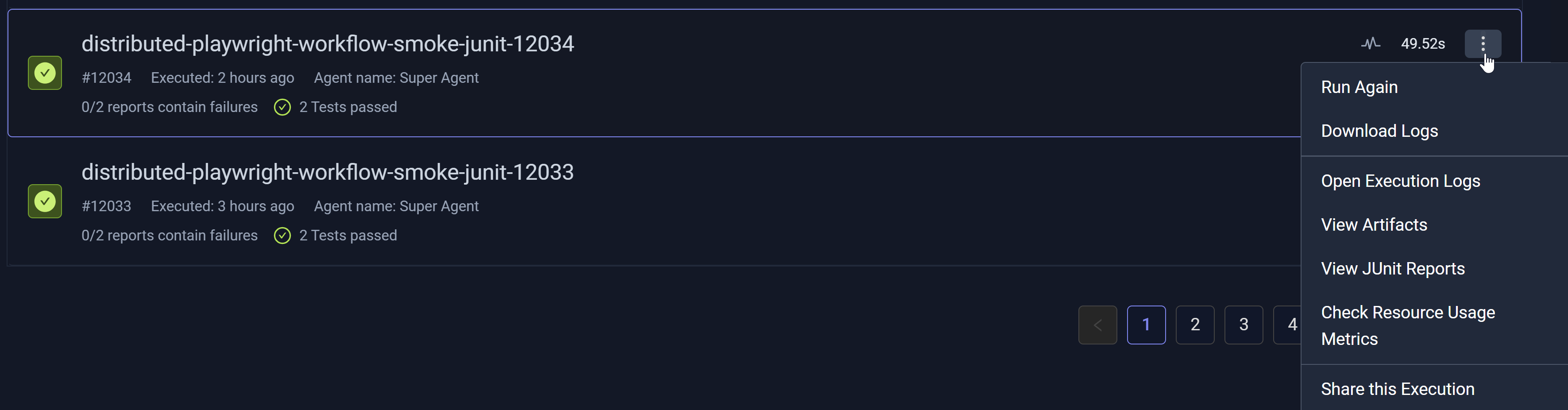
You can identify and select a Workflow Execution then choose More Options (three vertical dots) to view and make other selections.
You can also select an Execution from the list to view Execution-specific details. These details open in a new modal that contains the Log Output, JUnit Reports, Artifacts, Resource Usage, Flowchart, CLI Commands, Events, and Workflow Definition tabs. Run again allows you to re-execute the Workflow.
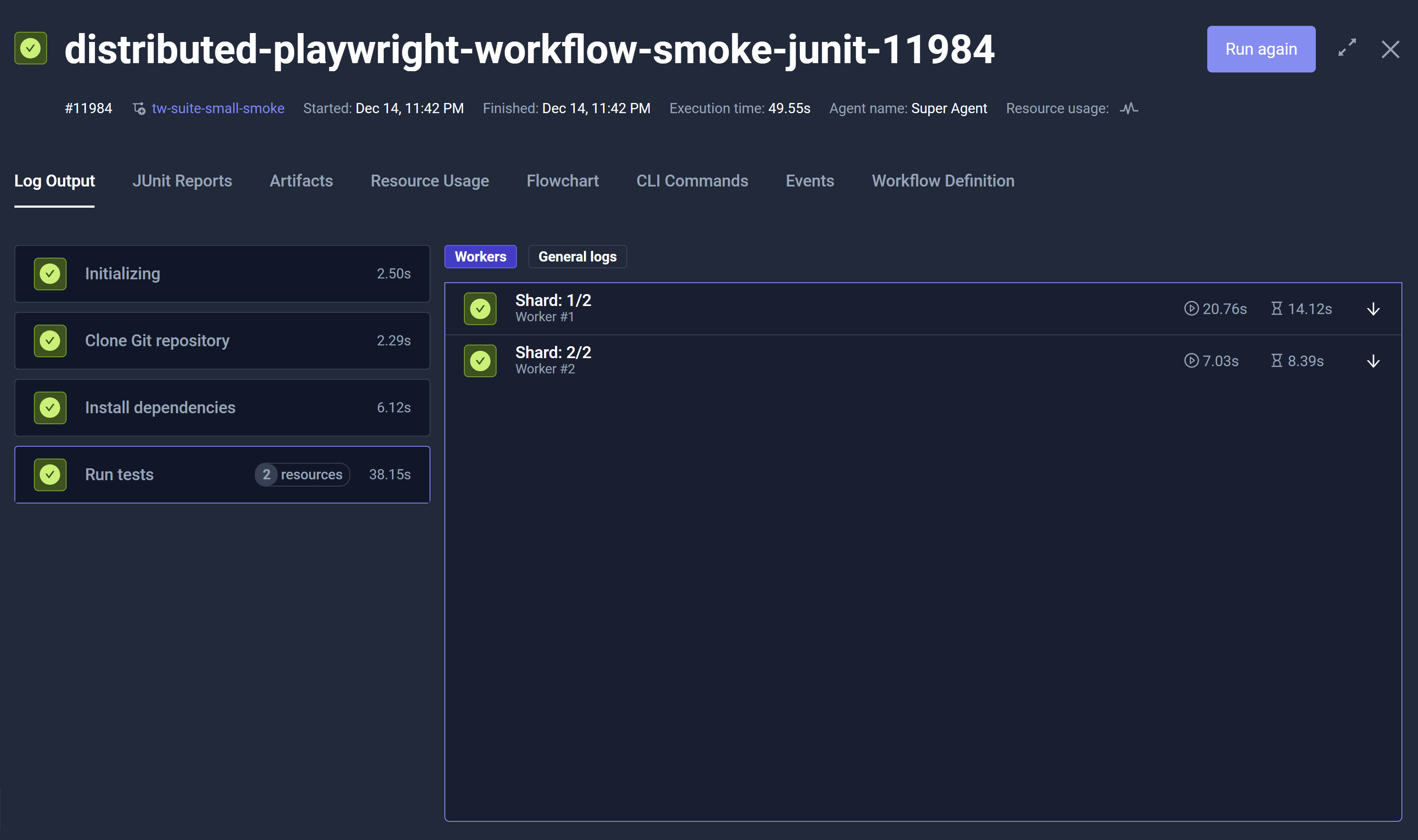
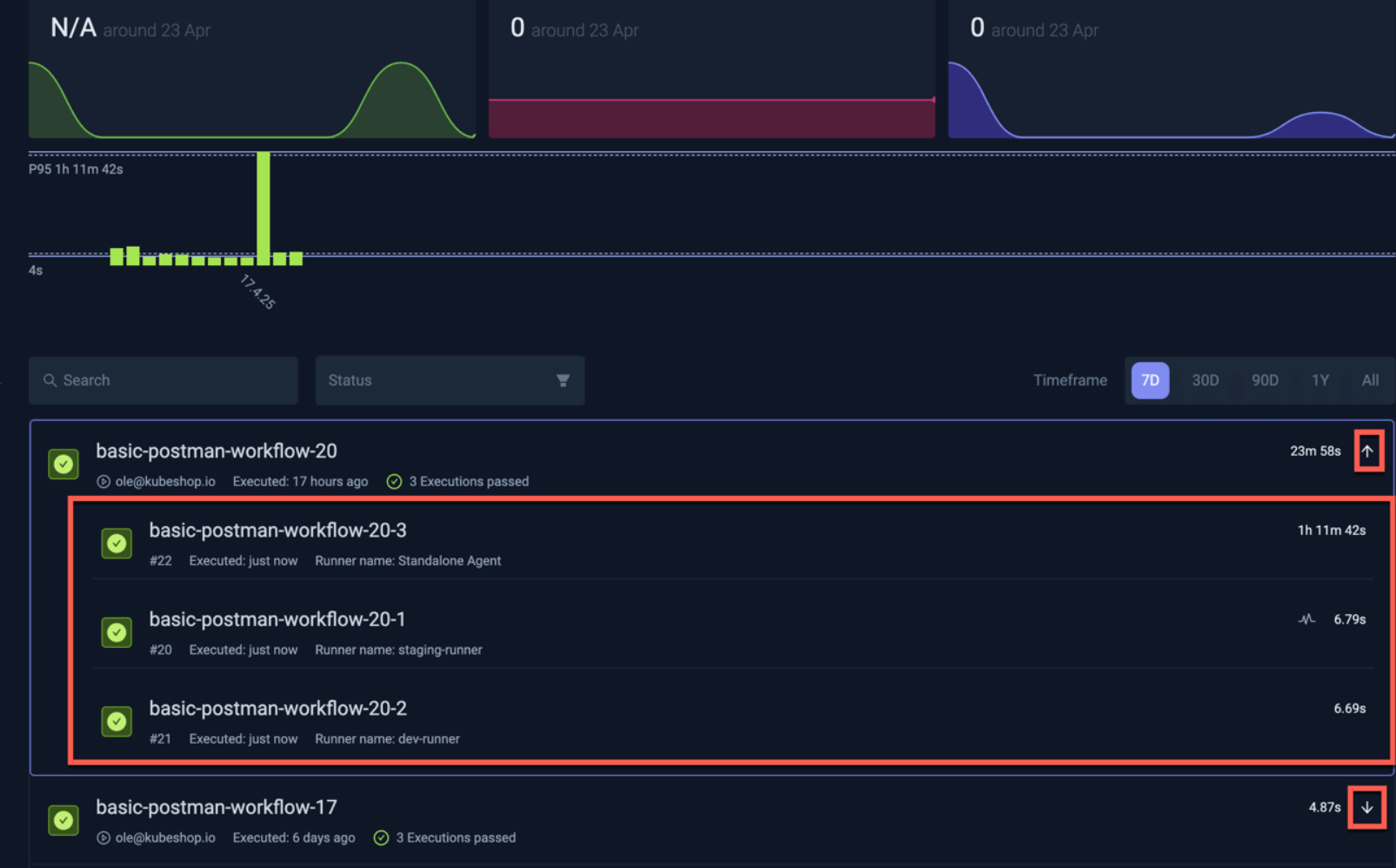
Multi-Agent Executions
For Executions that use multiple Runner Agents, an expandable section includes those Executions. Use the arrows to expand and collapse these Executions.
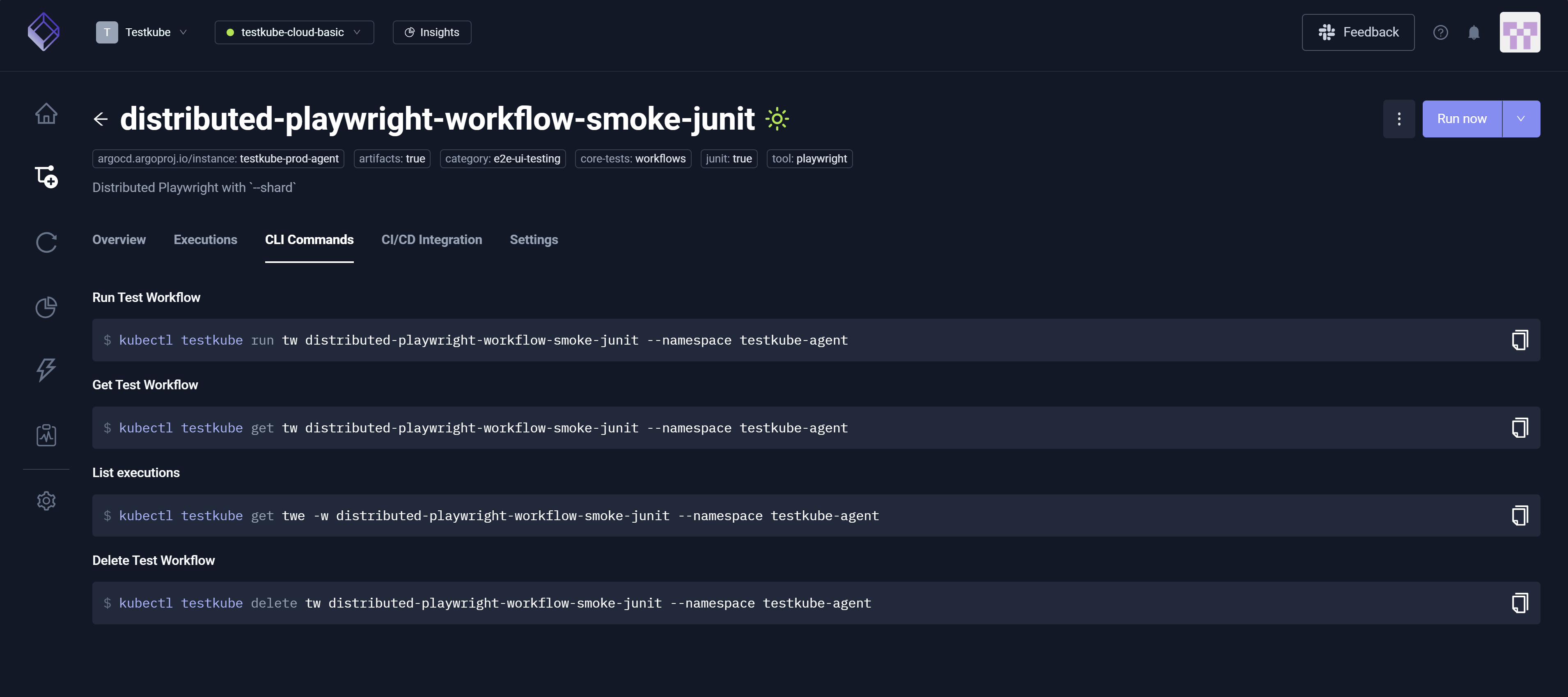
CLI Commands Tab
The CLI Commands tab displays CLI commands you can run to interact with the Workflow directly from the command line. You can execute Run Test Workflow, Get Test Workflow, List Executions, and Delete Test Workflow. For additional information, read Testkube CLI.
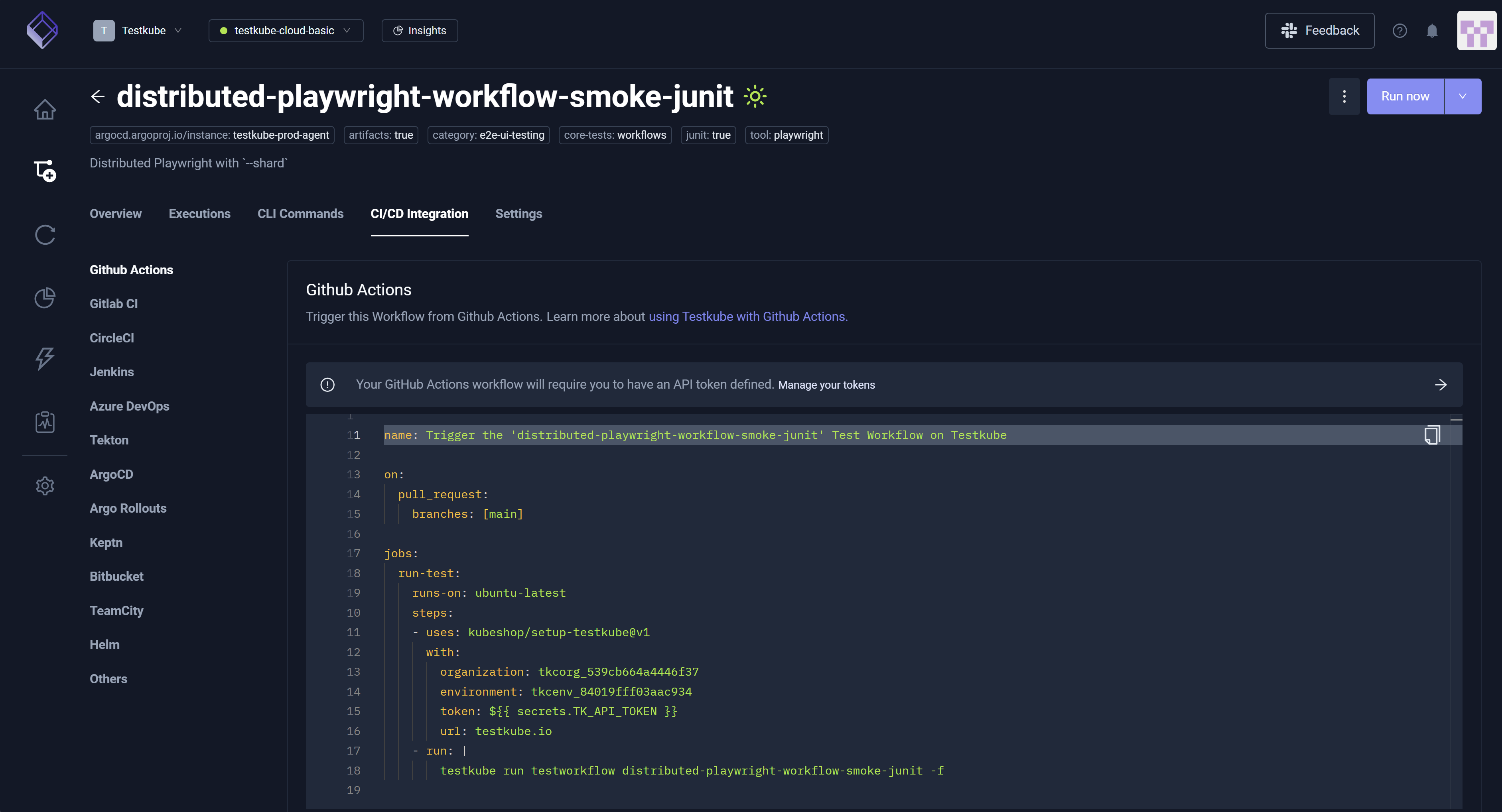
CI/CD Integrations Tab
The CI/CD Integration tab provides insight into how to trigger the Workflow from common CI/CD tools and includes ready-to-use examples for each. For additional information, read Testkube Integrations Overview.
You commonly run Workflows via this tab and Scheduling, accessible via Settings.
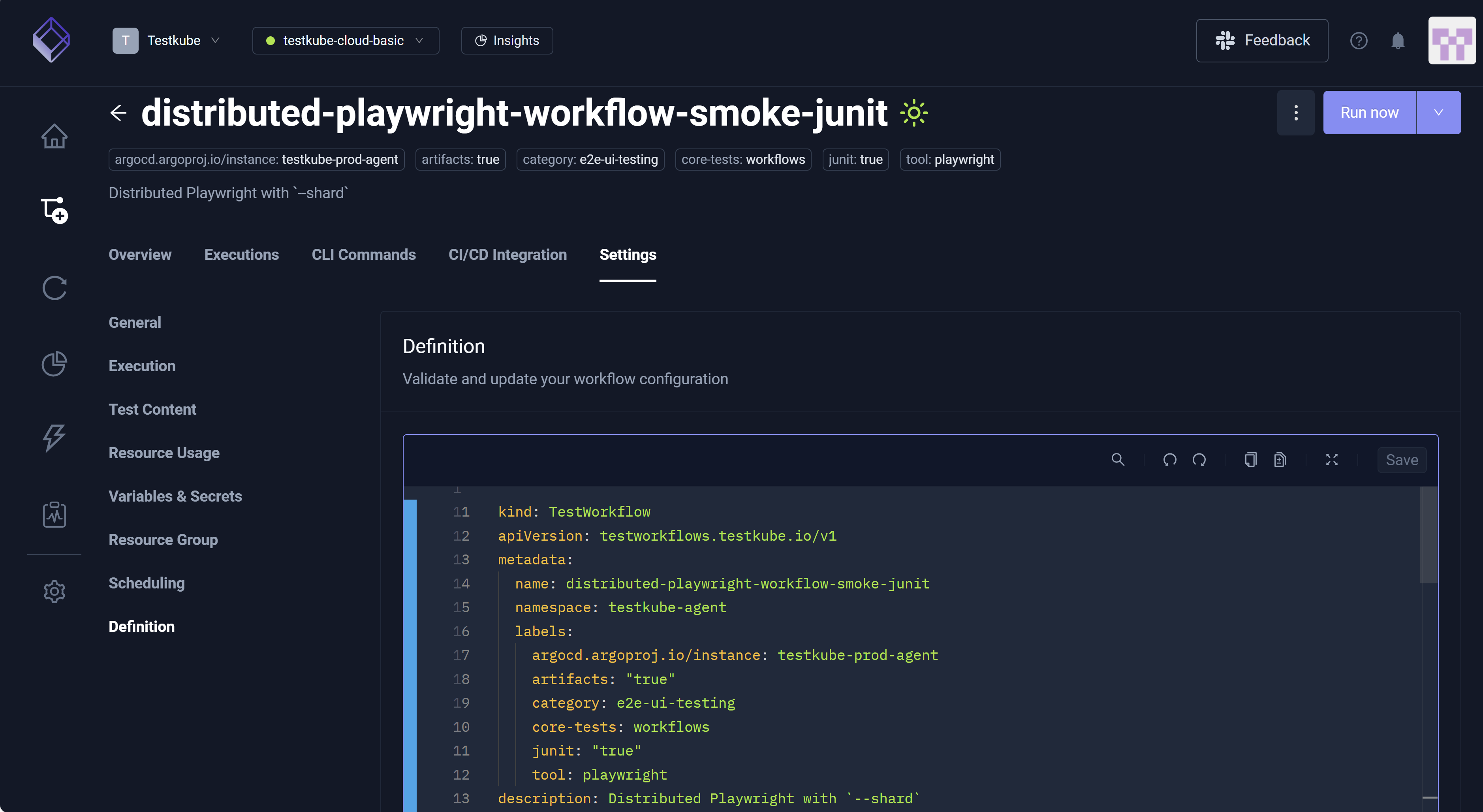
Workflow Settings Tabs
The Settings tab is the primary interface for building the YAML Definition, encompassing configurable settings such as General, Execution, Test Content, Resource Usage, Variables & Secrets, Resource Group, Scheduling, and Definition. More specifically, configuring these settings dynamically generates and updates the YAML visible via Definition. For example, designating 333 in the CPU field in the Resource Limits section of Resource Usage populates the corresponding resource/limits in the YAML file. You can configure Definition using the Settings configurations, or you can edit the YAML Definition directly.
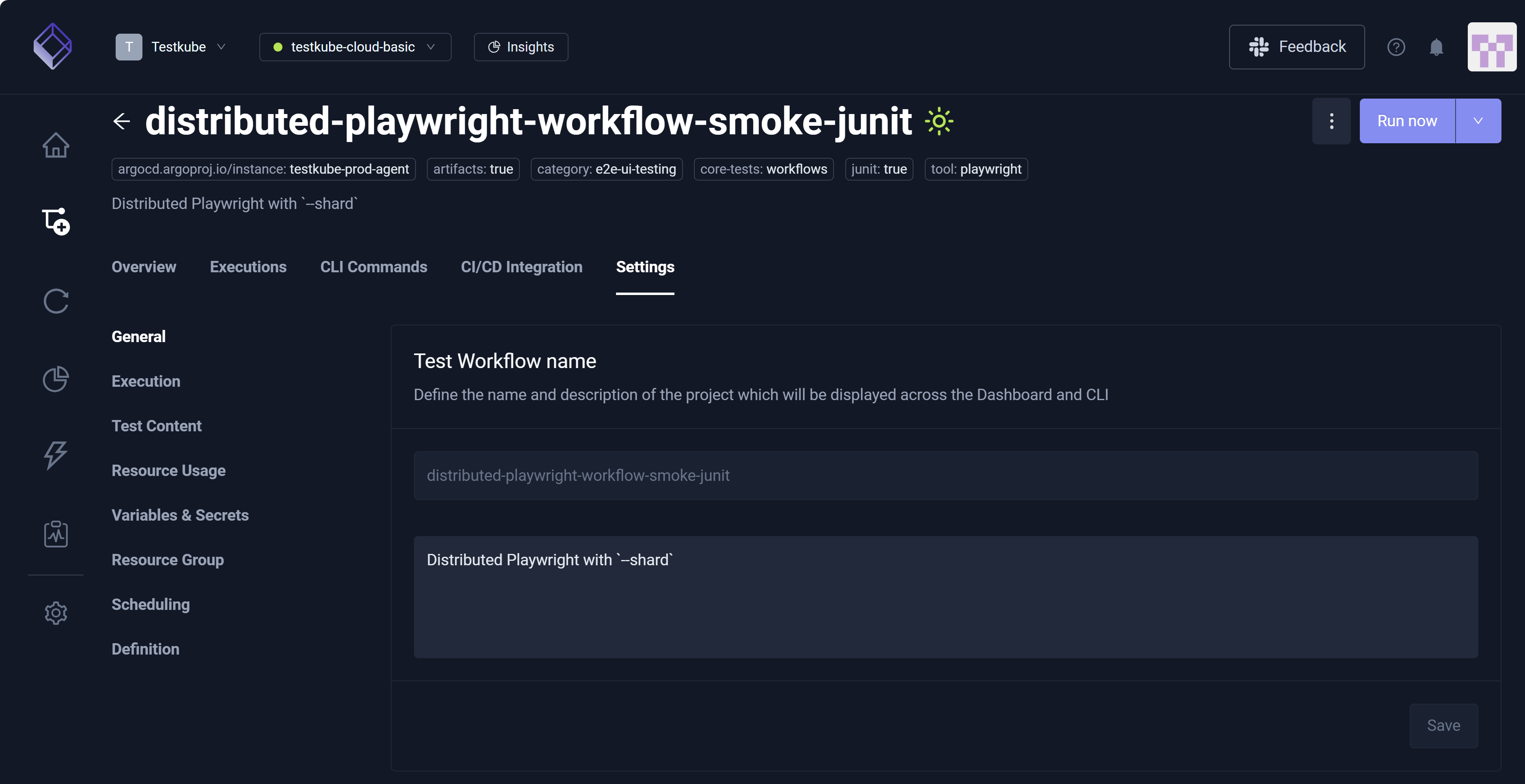
General
The General setting allows you to update:
- Test Workflow name – Title or designation you use to identify the Workflow.
- Labels – Tag you add to the Workflow for actions such as filtering and searching.
- Timeout – Workflow Execution expiration.
General also allows you to Delete this Test Workflow and Purge Past Executions; the latter makes database/storage space available if you have several old Executions for this Workflow.
Due to Kubernetes constraints, it is not possible to change the Workflow name. Instead, you must create a copy of the Workflow with the new name and delete the old one.
Execution
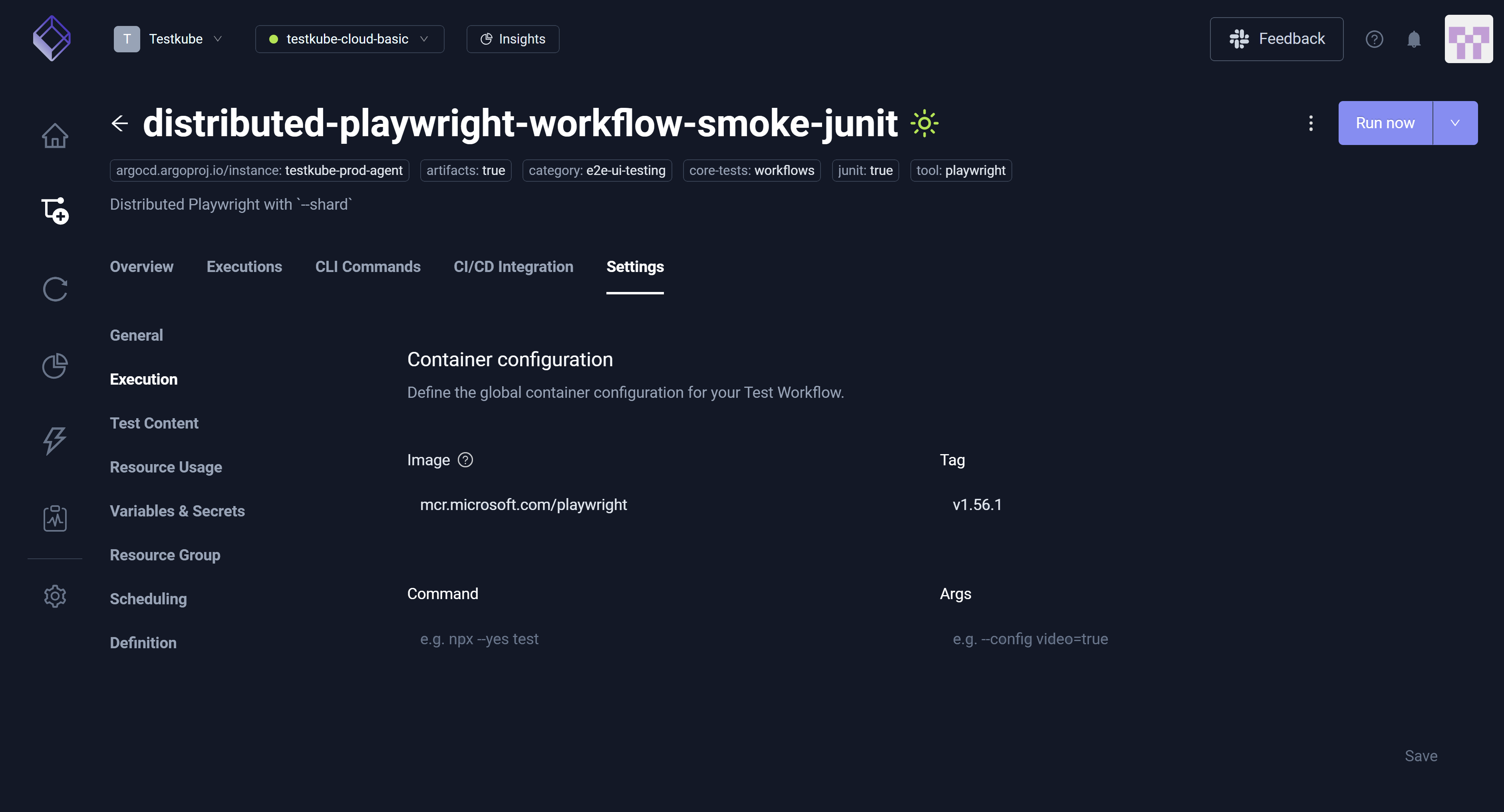
The Execution setting only applies to Workflows that use a single image and a single step – generally recommended when editing the Workflow YAML directly in the Definition setting to ensure changes are compatible with other constructs in your Workflow.
The Execution setting allows you to define Container configuration which includes Image, Tag, Command, and Args along with the Working directory. Collectively, you can use these settings to run your tests.
Test Content
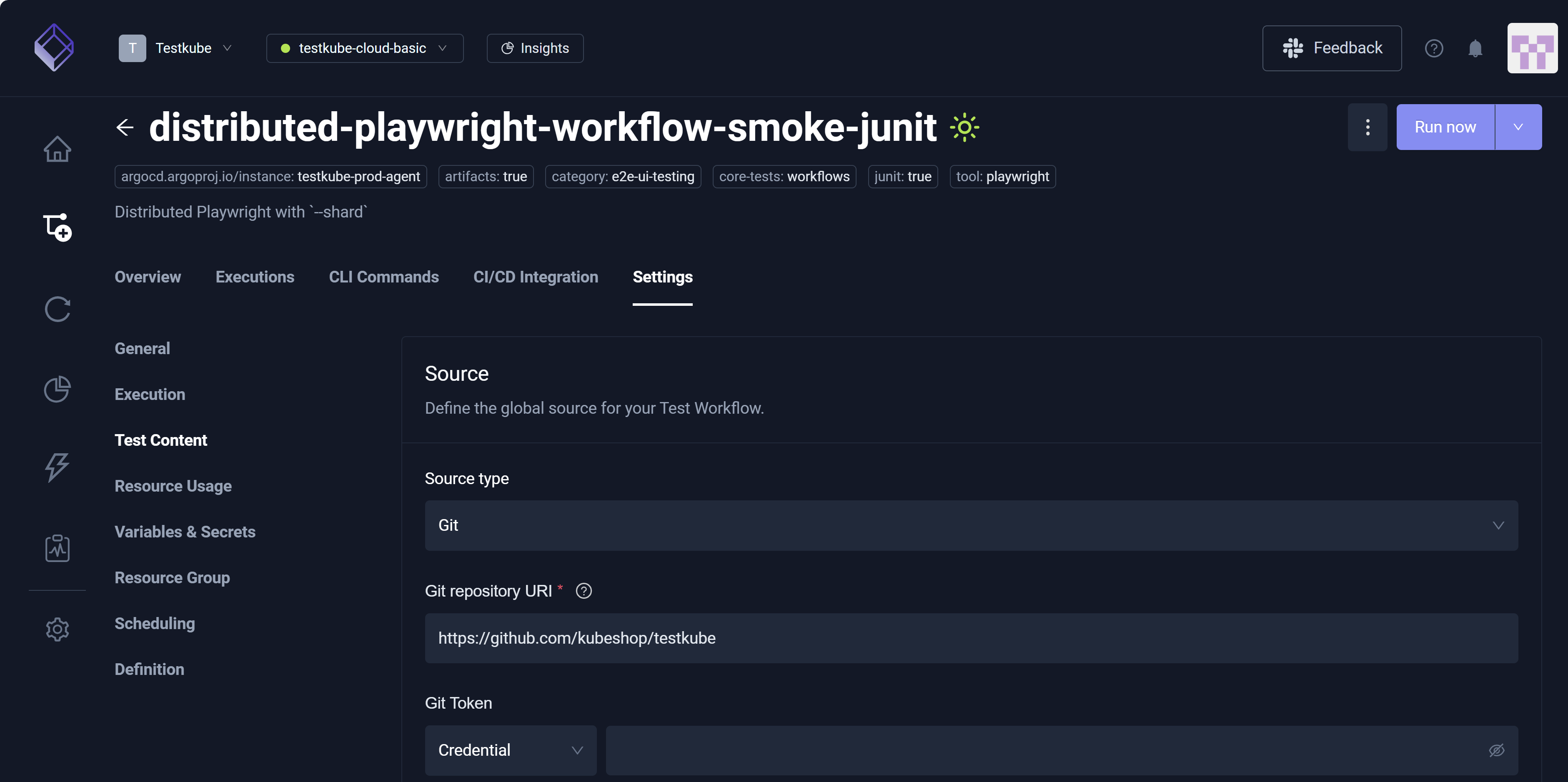
The Test Content setting only applies to Workflows that use a content Source for their tests. Use the Definition setting to edit the Workflow YAML directly if your Workflow uses more than one Source for its tests.
Resource Usage
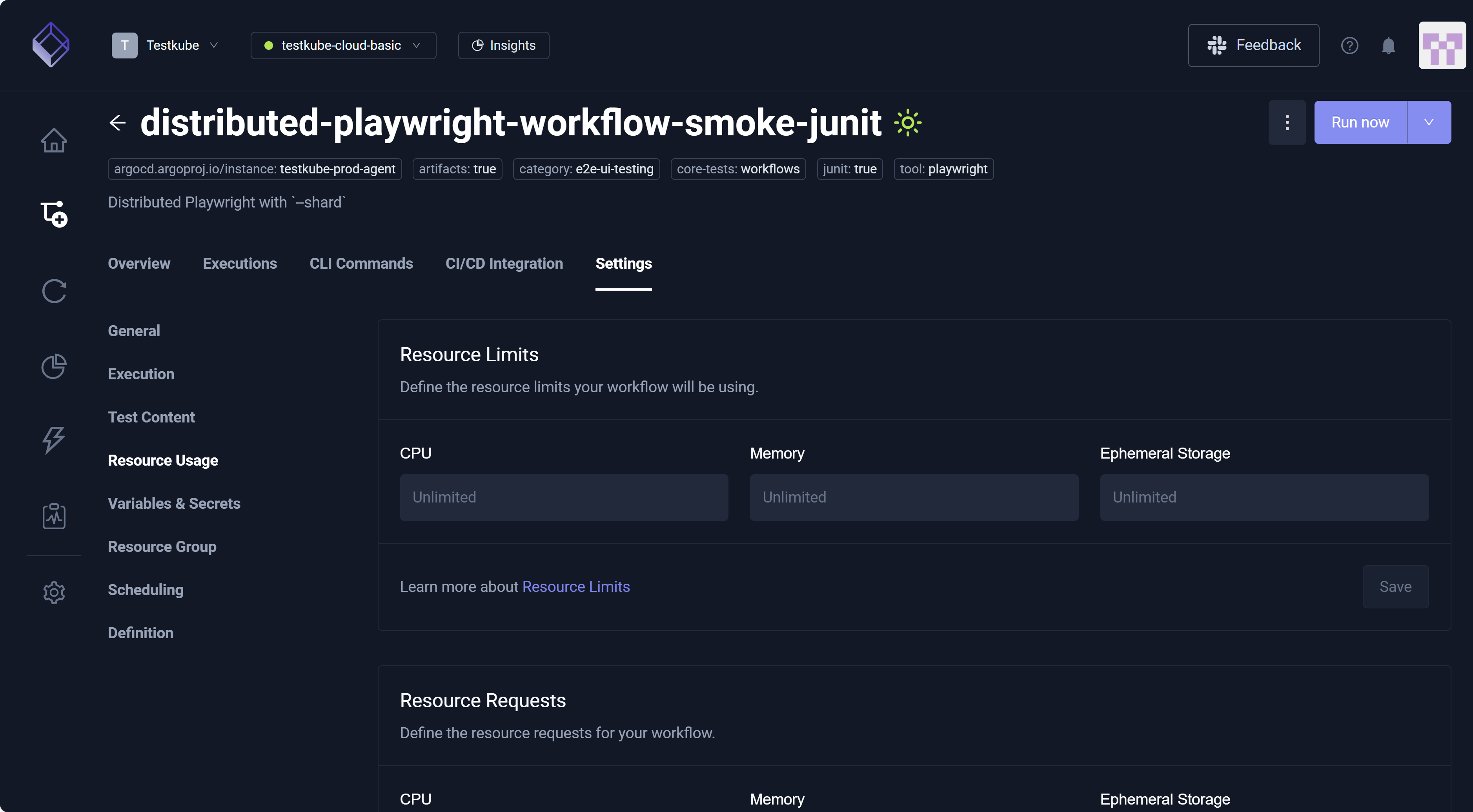
The Resource Usage setting allows you to establish CPU, Memory, and Ephemeral Storage for Resource Limits and Resource Requests.
The Resource Usage setting establishes global limits for resource usage within your Workflow. If you want to fine-tune these limits per image or Workflow step, you can do so directly in the Workflow YAML via the Definition setting.
Variables and Secrets
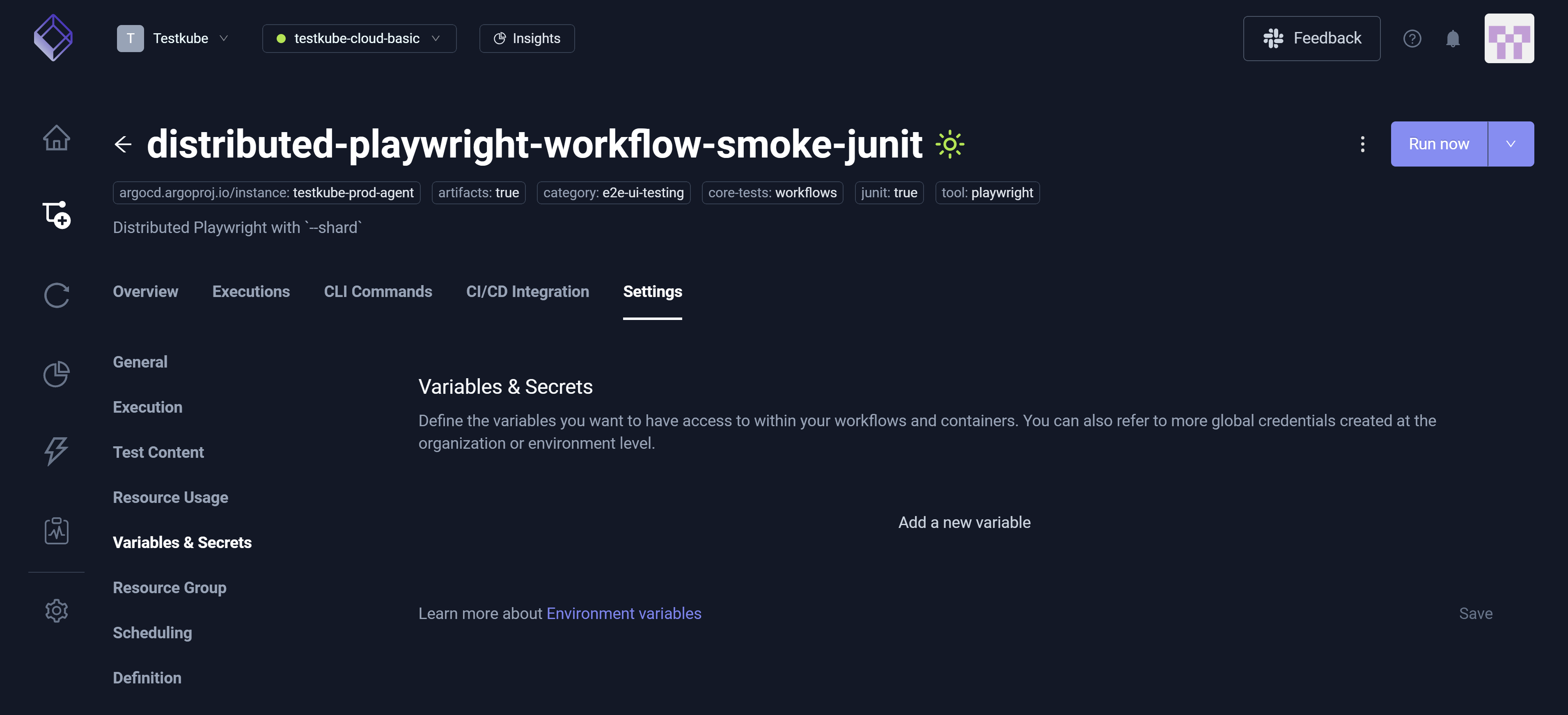
The Variables & Secrets setting allows you to define global variables and secrets used throughout the Workflow. You can also reference global credentials created at the Organization or Environment level.
Resource Group
The Resource Group setting allows you to assign this Workflow to a Resource Group. For additional information, read Resource Groups.
Scheduling
The Scheduling setting allows you to configure a single schedule for your Workflow, designating when and how often the Workflow runs. If you want to define multiple schedules, you can do so directly in the Workflow YAML via the Definition setting.
You commonly run Workflows via this setting and the CI/CD Integration tab.
For additional information, read Scheduling Workflows.
Definition
The Definition setting provides a powerful YAML editor for modifying your Workflows. As you designate various configurations via General, Execution, Test Content, Resource Usage, Variables & Secrets, Resource Group, and Scheduling, your specifications are automatically reflected in the YAML file. These settings, therefore, dynamically build this file. Some changes, however, you must make manually in the YAML file itself. For additional information, read Workflow YAML Editor.