Remote Workflow Execution
In a complex Testkube installation it might be desirable to schedule and synchronize the execution of Workflows across multiple Environments. Let's look at how Test Workflows can use the Testkube CLI to achieve this.
Using the CLI to trigger remote Workflows
You can automate the Testkube CLI in your Test Workflows to trigger the execution of a Workflow in another Environment and collect its results - allowing you to potentially aggregate executions and results from multiple environments in a single "Controller Environment".
To trigger a Workflow in another Environment using the Testkube CLI we need at least the following:
apiToken- an API Token generated for the remote Environment under its containing Organization - Read More.environmentId- the Testkube ID of the target Environment.organizationId- the Testkube ID of the organization containing the target Environment.rootDomain- the domain where the Testkube Control Plane is running - this will betestkube.iowhen using Testkube Cloud.workflowName- the name of the target workflow to run.
Below is an example Workflow that defines all the above as configuration parameters.
kind: TestWorkflow
apiVersion: testworkflows.testkube.io/v1
metadata:
name: run-remote-workflow
namespace: testkube
spec:
config:
apiToken:
type: string
default: tkcapi_XX
environmentId:
type: string
default: tkcenv_XX
organizationId:
type: string
default: tkcorg_XX
rootDomain:
type: string
default: testkube.io
workflowToRun:
type: string
steps:
- run:
image: kubeshop/testkube-cli:latest
shell: |
testkube set context \
--api-key {{ shellquote(config.apiToken) }} \
--root-domain {{ shellquote(config.rootDomain) }} \
--org-id {{ shellquote(config.organizationId) }} \
--env-id {{ shellquote(config.environmentId) }}
testkube run tw {{ shellquote(config.workflowToRun) }} -f
Check out all available testkube run tw parameters in the CLI Reference.
Passing Configuration Parameters
If the target Workflow accepts configuration parameters, we can add these to the testkube run tw command with the --config
parameter, for example if the Workflow triggered in the example above requires a name parameter, this would be specified
as follows:
testkube run tw {{ shellquote(config.workflowToRun) }} -f --config name=SomeName
Log Output from Remote Workflows
The -f parameter specified in the example above will wait for the target Workflow to finish and capture its log output
to stdout, allowing you to see and analyse the remote execution log from the calling Workflow logs. For example the
below output for the above Workflow was generated when calling a target Workflow that runs a simple CURL command:
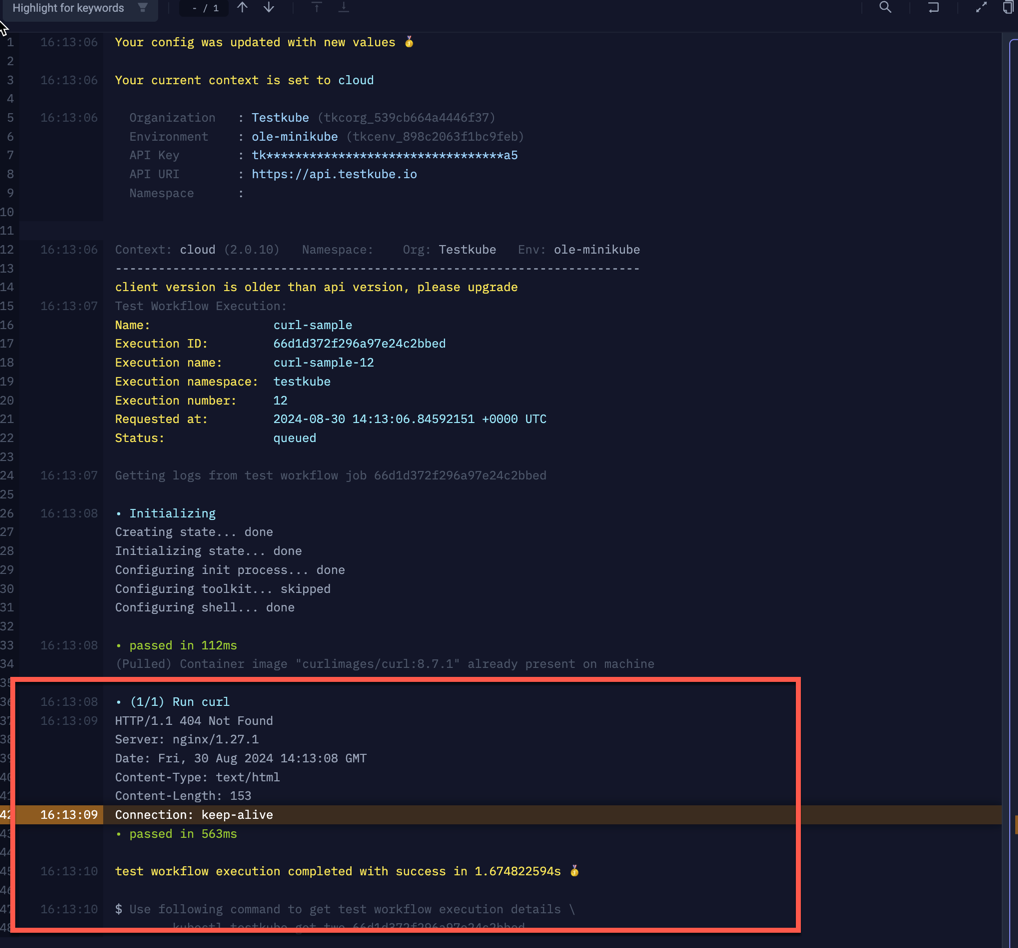
The highlighted section is the actual CURL output, everything above that is related to the testkube set context command
and the subsequent call to testkube run tw.
Artifacts from Remote Workflows
If the target Workflow generates artifacts, we can modify the shell command above as follows:
...
shell: |
testkube set context \
--api-key {{ shellquote(config.apiToken) }} \
--root-domain {{ shellquote(config.rootDomain) }} \
--org-id {{ shellquote(config.organizationId) }} \
--env-id {{ shellquote(config.environmentId) }}
mkdir /data/artifacts
testkube run tw {{ shellquote(config.workflowToRun) }} -f -d --download-dir /data/artifacts
artifacts:
paths:
- /data/artifacts/**/*
The following changes were made:
- a
mkdir /data/artifactscommand to create a folder for artifacts. - additional
-d --download-dir /data/artifactsarguments to thetestkube run twcommand. - an
artifactsproperty telling Testkube where to find the downloaded artifacts Learn More.
The following example output is from a remote Playwright test that was configured to generate both reports and traces:
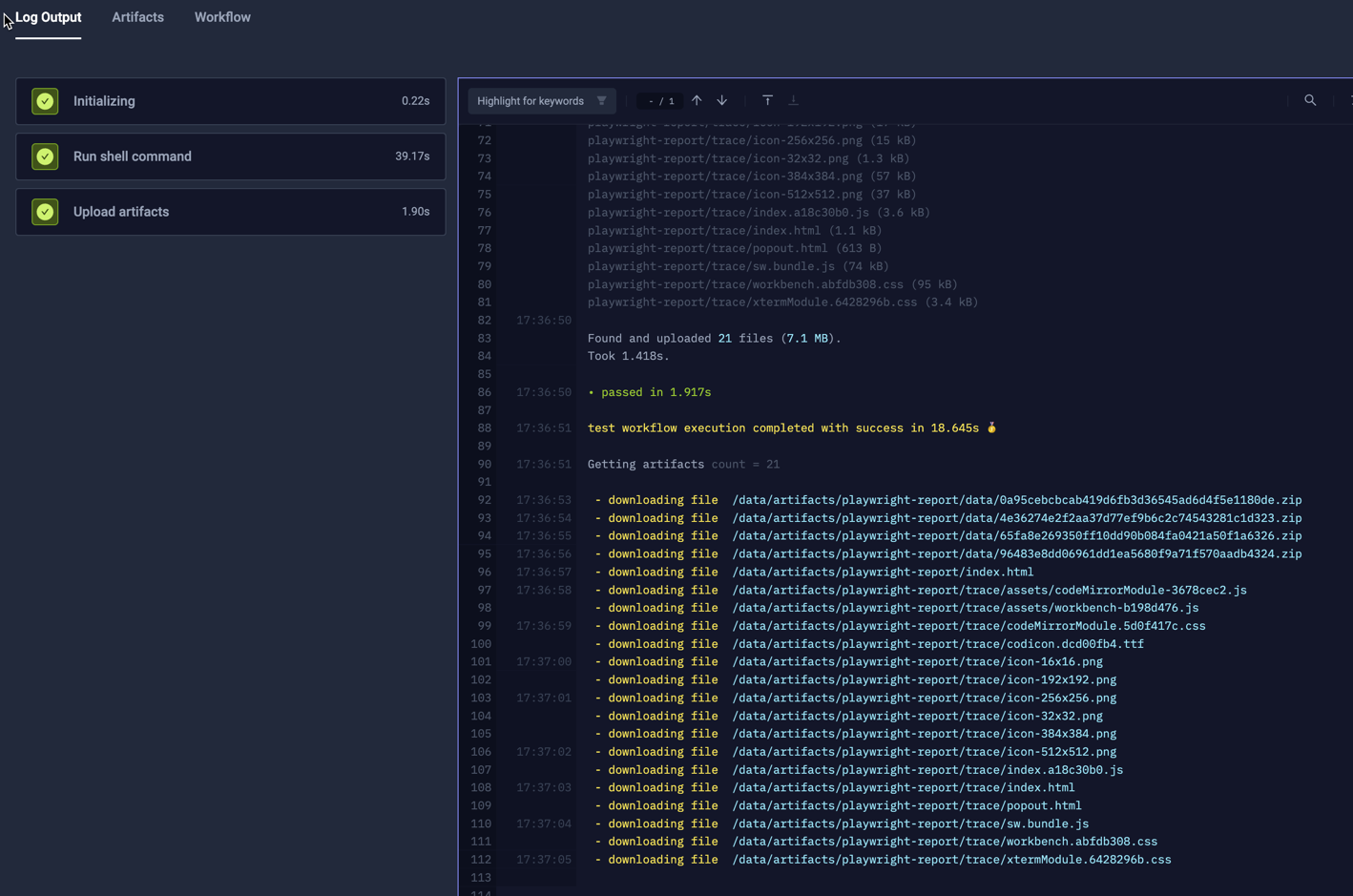
These artifacts are now available for viewing under the Artifacts Tab:
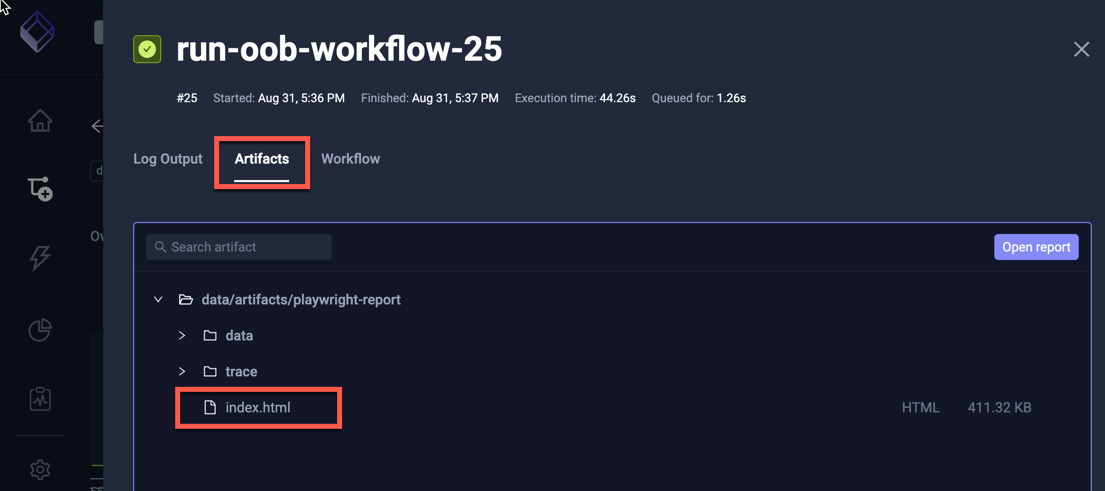
Synchronized Multi-Enviroment Execution
It can sometimes be desirable to coordinate the execution of Workflows across multiple Testkube Environments, for example if you want to synchronize tests to run from different geographical locations against an external target, or if you want to validate application functionality/access from both inside and outside the cluster the application is running in.
Combining the above with the approach described in Test Suites allows
you to do this with Testkube; simply create a dedicated Workflow that uses execute to trigger both remote and local
Workflows as desired.
kind: TestWorkflow
apiVersion: testworkflows.testkube.io/v1
metadata:
name: multi-environment-e2e-test
spec:
steps:
- execute:
workflows:
- name: e2e-test
config:
targetUrl: <internal-hostname>
- name: run-remote-workflow
config:
apiToken: tkcapi_XXXX
environmentId: tkcenv_XXXX
organizationId: tkcorg_XXXX
targetUrl: <external-hostname>
workflowToRun: basic-load
- name: run-remote-workflow
config:
apiToken: tkcapi_YYYY
environmentId: tkcenv_YYYY
organizationId: tkcorg_YYYY
targetUrl: <external-hostname>
workflowToRun: basic-load
The above example executes
- a local
e2e-testWorkflow that runs an end-to-end test against an application to be tested. - two
basic-loadtests in separate Testkube Environments, each putting load on the same application to be tested.
The purpose of this specific setup is to validate that our application is fully functional when under load from two external sources, but you could for example create similar scenarios where multiple tests are combined both in sequence and in parallel to ensure that your target applications and services perform in line with their requirements under complex usage scenarios.